Hi, I’m Kiel Johnson: a UI/UX Designer from Boise, Idaho.
I help companies create beautiful & intuitive digital experiences for SAAS companies.
Proficiencies:
UX Design (Journey Mapping, Wireframing & Prototyping)
Digital Product Strategy
User Research / Testing
Responsive Web Frontend Coding
Brand Strategy
Agile and Shape-up team management
Tools:
Figma / Figjam
Jira / Confluence
Adobe Creative Cloud
Framer
Optimal Workshop
Education
BFA in Graphic Design from Boise State University
12 Years Digital Work Experience
UX Case Studies
-
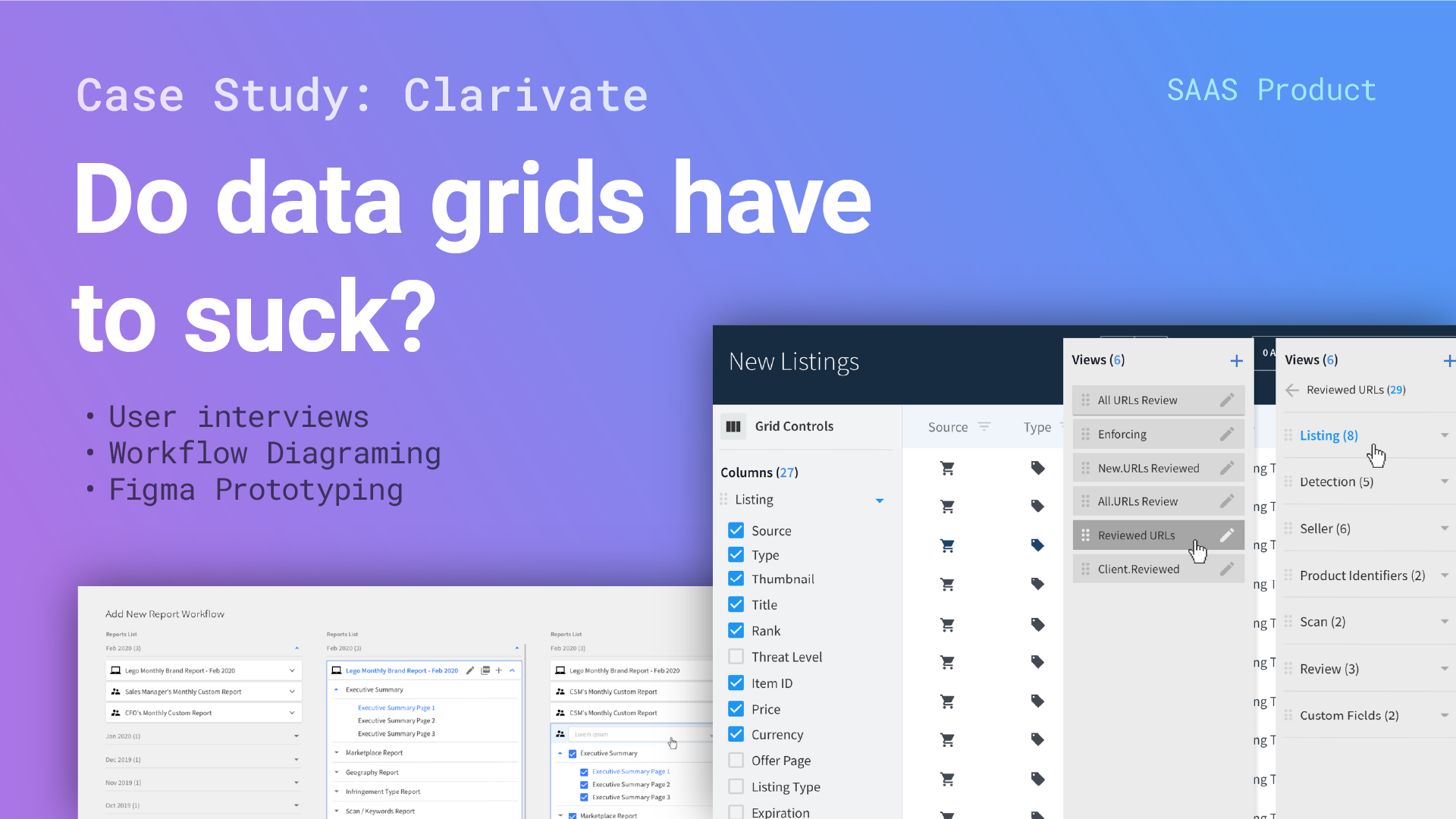
Clarivate Analytics
A cyber security company’s captive user pool struggled with managing large amounts of data.
-

Kount Platform
After multiple product acquisitions, Kount needed to freshen up their legacy product and leverage new features at the same time.
-

Grow it.
It all begins with an idea. Maybe you want to launch a business. Maybe you want to turn a hobby into something more.
Manifesto
When possible, do less
“Good design is as little as possible. Less, but better, because it concentrates on the essential aspects, and the products are not burdened with non-essentials. Back to purity, back to simplicity.”
-Dieter Rams, Less but Better
Utilize Design Thinking
Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test are the 5 steps on the design thinking process as defined by the interaction design foundation.
-IDF, Design Thinking
Keep Learning
It’s important to stay on top of visual trends, tech changes, and industry leading resources like Medium, Nielson Norman group, and the Interactive Design Foundation to be constantly improving.
-Me
My Design Process
Start with Design Thinking
“Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. It is most useful to tackle ill-defined or unknown problems”
Step 1: Empathize
Aim to understand the problem through user research.
Step 2: Define
Analyze the observations and synthesize them to define the core problems into problem statements.
Step 3: Ideate
Workshop alternative ways to view the problem and identify innovative solutions to the problem statement.
Step 4: Prototype
Identify the best possible solution for each problem via experimental prototypes.
Step 5: Test
Test the prototypes with real users to evaluate how effectively they solve the problem.
Evaluate Product Effectiveness
A product must be Feasable (Engineering Stakeholder), Viable (Business Stakeholder), and Desireable (Design Stakeholder).
Feasibility - a product that can be created with new or existing technology
Can we develop the technology for this product? How long will it take? How much will it cost? How will the product be distributed so the right people can use it?
Viability - a product that will be profitable
Who will be willing to pay for the product? How they will pay for it? Will this add up to profitability?
Desirability -a product that people want or need
Is there a problem? Is our solution solving it? Is the experience great?
